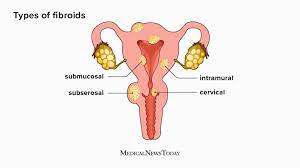
Fibroids: Understanding the Common Women’s Health Issue
Fibroids, also known as uterine leiomyomas, are a common health issue that affects women of reproductive age. These non-cancerous growths form in the muscle tissue of the uterus and can range in size from small, undetectable nodules to large, noticeable masses. While some women may not experience any symptoms related to fibroids, others can experience severe discomfort and other complications that can impact their daily lives. In this article, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of fibroids.
Causes of Fibroids
The exact cause of fibroids is not well understood. However, research suggests that they develop due to a combination of factors, including genetics, hormones, and growth factors. Family history is a significant risk factor for developing fibroids, and women with a mother, sister, or daughter who has been diagnosed with fibroids are more likely to develop them as well. Estrogen and progesterone, the hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle, also play a role in fibroid development. Fibroids tend to grow during times of high hormonal activity, such as during pregnancy or when taking hormone replacement therapy. Additionally, growth factors such as insulin-like growth factor may stimulate fibroid growth.
Symptoms of Fibroids
Many women with fibroids do not experience any symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they can range from mild to severe. Common symptoms of fibroids include:
- Heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding
- Pelvic pain or pressure
- Painful intercourse
- Frequent urination
- Constipation
- Backache
- Abdominal swelling
In some cases, fibroids can also lead to infertility or complications during pregnancy.
Diagnosis of Fibroids
Fibroids are often diagnosed during a routine pelvic exam or ultrasound. If a fibroid is detected, additional testing, such as an MRI or hysteroscopy, may be recommended to determine its size and location. These tests can also help rule out other conditions, such as ovarian cysts or endometrial cancer.
Treatment of Fibroids
Treatment for fibroids depends on the severity of symptoms, the size and location of the fibroids, and the patient’s age and desire for future fertility. In many cases, no treatment is necessary, and the fibroids are simply monitored for changes. However, when symptoms are severe or the fibroids are causing complications, treatment may be necessary.
Medical treatments for fibroids include:
- Hormonal therapy: Medications that regulate hormone levels and can reduce the size of fibroids.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Over-the-counter pain relievers that can reduce pain and inflammation caused by fibroids.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRH agonists): Medications that can shrink fibroids by reducing hormone levels.
Surgical treatments for fibroids include:
- Myomectomy: A surgical procedure to remove fibroids while leaving the uterus intact. This is often recommended for women who want to have children in the future.
- Hysterectomy: A surgical procedure to remove the uterus. This is recommended for women who have severe symptoms or who are no longer interested in having children.
In conclusion, fibroids are a common health issue that affects women of reproductive age. While many women with fibroids do not experience any symptoms, those who do can experience severe discomfort and other complications that can impact their daily lives. If you are experiencing symptoms related to fibroids, it is important to talk to your healthcare provider about treatment options that are right for you.