Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a type of bacteria that infects the stomach and is responsible for various gastrointestinal disorders. It is estimated that more than half of the world’s population has H. pylori, and it is one of the most common bacterial infections in humans.
The infection usually occurs during childhood, and if left untreated, it can lead to various health problems such as gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, and even stomach cancer. In this article, we will discuss H. pylori disease, its symptoms, causes, and treatments.
What is H. pylori disease?
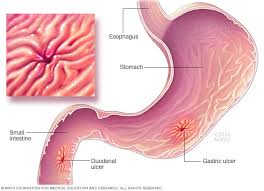
H. pylori disease is a bacterial infection that affects the stomach and small intestine. It is primarily transmitted through contaminated food and water or through contact with an infected person’s saliva, vomit, or feces.
The bacteria enter the body and attach themselves to the stomach lining, where they produce substances that weaken the protective mucus layer of the stomach. This causes inflammation and damage to the stomach lining, which can lead to the development of ulcers and other digestive problems.
Symptoms of H. pylori disease
H. pylori disease can cause various symptoms, including:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Nausea or vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating or belching
- Weight loss
- Fatigue
- Bad breath
In some cases, H. pylori infection can be asymptomatic, meaning there are no visible symptoms. However, even if there are no symptoms, the infection can still lead to complications such as ulcers and stomach cancer.
Causes of H. pylori disease
The primary cause of H. pylori disease is the bacteria itself. The bacteria are usually transmitted through contaminated food and water or through contact with an infected person’s saliva, vomit, or feces.
Some risk factors that increase the likelihood of developing H. pylori disease include:
- Living in overcrowded or unsanitary conditions
- Having a weakened immune system
- Smoking cigarettes
- Regular use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Diagnosis and Treatment of H. pylori disease
If you suspect that you have H. pylori disease, your doctor will likely perform a physical exam and order some tests to diagnose the infection. The most common diagnostic tests for H. pylori include blood tests, stool tests, and breath tests.
If the tests confirm the presence of H. pylori, your doctor may prescribe a combination of antibiotics and acid-reducing medications to eliminate the bacteria and reduce the risk of complications. The most common antibiotics used to treat H. pylori are clarithromycin, amoxicillin, and metronidazole.
In addition to antibiotics, your doctor may also recommend acid-reducing medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 blockers to reduce the amount of acid in your stomach and promote healing of the damaged stomach lining.
Prevention of H. pylori disease
To reduce your risk of H. pylori infection, it is important to practice good hygiene and food safety measures. This includes washing your hands regularly, avoiding contact with contaminated vomit or feces, and properly storing and cooking food to prevent contamination.
If you have been diagnosed with H. pylori disease, it is important to follow your doctor’s treatment plan and take all prescribed medications as directed. Completing the full course of antibiotics is crucial to ensure that the bacteria are fully eliminated and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Conclusion
H. pylori disease is a common bacterial infection that affects the stomach and small intestine. It can cause various symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite, and can lead to complications such as ulcers and stomach cancer if left untreated.